Location Classes¶
After creating a new crash point, the next step is to define its location class. Location classes are used to control how the system assigns all other attributes to the new crash point.
These classifications are defined by CGIT for the purpose of this project under guidance from the Highway Safety Office and VDOT. Use the following descriptions and examples to determine the proper location class to select.
Location class selection window.
Intersection¶
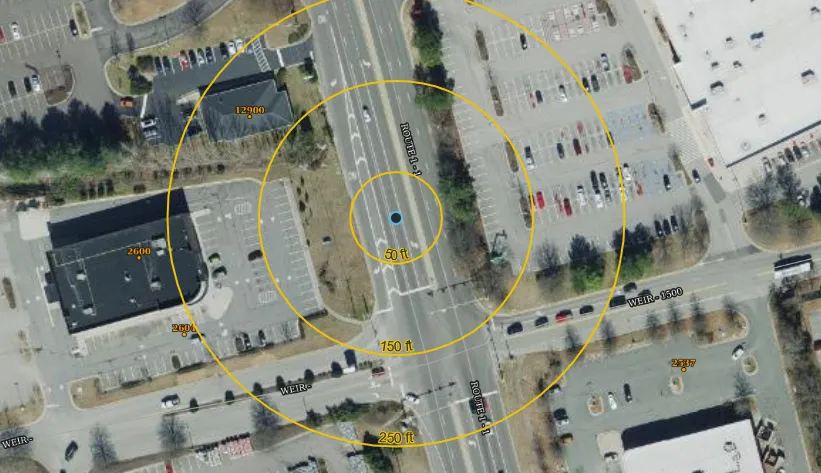
A crash is classified as at intersection if it occurred in the intersection or within a distance from the intersection.
- Large intersections, with more than two lanes of travel for both the primary and secondary roads, would use a buffer of 250 feet from the perceived white line.
- Medium intersections, with at least two lanes of travel on the primary road, use a buffer of 150 feet.
- Smaller intersections, such as neighborhood roads, would use a buffer of 50 feet.
Example intersection sizes.

All crashes that occur within the appropriate buffer of an intersection are considered ‘At Intersection’ crashes. This distinction is based purely on the location of the point created and not the cause of the crash. Crashes that involve deer, parked cars, parking lot entrances, or other unrelated characteristics within the intersection buffer are still treated as ‘At Intersection’ crashes. Additional information provided by the police officer is used to identify if a crash is related to the intersection.
Radius rings for 50, 150, and 250 feet.
Address¶
Any crash that did not occur at an intersection nor on an interstate highway (I-##) belongs to the address location class.
Interstates¶
If a crash is located on an interstate or an interstate ramp, it is considered an interstate location class. State or US routes and highways (i.e. VA-288, US-460) are not considered interstates. Be sure to only use this classification for interstates. Look for the proper formatting of ‘I-##’.
Parking Lot¶
If the crash occurred in a parking lot, the crash location should be classified as a parking lot. Since the crash did not occur on the road itself, only the address number and street name should be included. Use the road information that best defines the entrance to the parking lot. Parking lot crashes will later be evaluated by the highway safety office to determine if the crash is considered reportable.
Parking Lot Exception
The one exception is if the crash occurs in an interstate rest area. If the only way in and out of the rest area is from an interstate, it should be classified as an interstate crash and the street name should be “I-## REST AREA”.
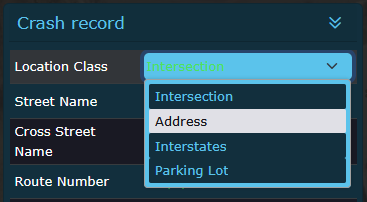
Changing the location class¶
If the selected location class needs to be changed, click on the location class field in the left sidebar. This will open a drop-down to select another option.
Editing a location class.
Next: Assign Road Attributes¶
Once the location class is set, you are ready to begin assigning the road attributes to the crash record. Continue to 'Assign Road Attributes' for remaining steps.